- HubPages»
- Technology»
- Computers & Software»
- Computer Science & Programming
Simple Steps to Start Developing Mobile Applications (Cellphone APPS) in Java
Introduction
If you're searching for some simpler ways and methods to familiarize yourself with world of "Mobile Application Development", then, I think you finally landed on correct destination (article). Here, I'll show you all the steps that are required in understanding and making usage of this great platform of Application Development, which will help you in reaching pockets of humans without going there. I called Mobiles / Cellphones a great platform because this is the platform which remains active nearly 24 hrs a day either in hands of people or in pockets and can be accessed by users (i.e. owners of devices) at anywhere and at anytime. It is one of the most nearest and closest part of everyone (Who use them).

Programming Language for Developing Mobile/Cellphone APPS
There are lot of languages and tools by which you can develop mobile apps but problem arises when some devices failed to install/run our applications due to limited device compatibility. But, there exist a language called Java ME (j2me) (A smaller form of java , which has been released to cover cellphone market) and is supported by maximum number of devices in this market. Here, "ME" in Java ME is shorter form of "Micro Edition". It divides devices into two type of configuration i.e. CLDC and CDC, which is explained below.
- CLDC - Connected Limited Device Configuration,
- CDC - Connected Device Configuration.
"CLDC" includes the range of phones which are unable to support full features of java due to limitations in storage, memory and power etc., while on other hand range of phones falling in "CDC" category doesn't have such shorter limits and they also have their own plus points. Let's end up our discussion here and come to procedure. Here, Below aresteps that are required in building up your first cellphone/mobile application.
Installing and running Java ME (Micro Edition) SDK (Software Development Kit)
These section deals with steps that are required to be followed at minimum before developing your first cellphone application, just follow them.
- Download Java ME SDK (3.0 or Latest Version) from here (I'm using Java ME SDK 3.0 and it is my personal recommendation to start with).
Software and System Requirements:
- Java SE Development Kit - JDK 1.6 or latest,
- NetBeans version 6.9 or higher for installing Java ME SDK 3.0.5 and higher versions, which is not my personal recommendation for beginners while considering my future tutorials in mind.
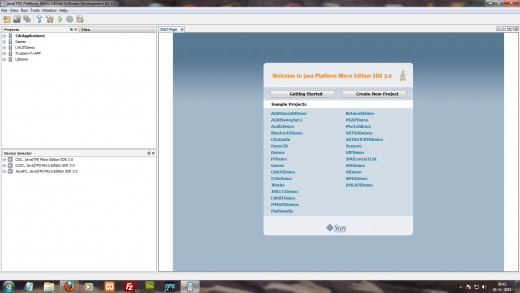
- After fulfilling the system requirements by downloading and installing necessary softwares, Click on executable (.exe) file of Java ME SDK to install and make it run. Below is the sample snapshot of Java ME SDK 3.0 (similar to its first run).
Creating and Editing your first Mobile APP
This section covers the steps that are required in creating and developing your first cellphone APP (i.e. a simple hello world program) with this SDK.
- After Installing, Go To Start -> Programs -> Java(TM) ME Platform SDK 3.0 -> Java(TM) ME Platform SDK 3.0 OR if you downloaded and installed 3.0.5 or higher versions, then, go to Go To Start -> Programs -> NetBeans -> (NetBeans IDE 7.0.1 or any which is installed on your computer).
- Then, after opening SDK, Go to File (Top-Left Corner) -> New Project -> Java ME -> MIDP (or mobile) Application -> Next (At Bottom) -> Next - > Finish.
- And, Finally A screen will appear on your screen with some j2me code in it. This is the Code which is required at minimum by any j2me (Mobile/Cellphone) application for proper functioning. I would not recommend to delete it because it will never interfere in your development cycle except the "startApp()" function which plays crucial role in beginning of application life cycle.
In simpler terms, "startApp()", "pauseApp" and "destroyApp" are life cycle functions of any application which executes automatically at three different states of any applications which are explained below.
- "startApp()" - executed on top of everyone to begin application life cycle.
- "pauseApp()" - get executed when application goes in state of being paused i.e. user has moved his focus from current application to some other tasks in his/her device. for example, when a phone call comes in between the usage of this application by user, application automatically goes into pause state.
- "destroyApp()" - get executed when user exits the application i.e. termination of life cycle.
Running your First Application
This section deals with steps that are required in running your first mobile application ("Hello World!" program).
You can run your application in three type of modes either from menu bar (by clicking on "RUN") or by right clicking on project.
- Either you can run directly, which will skip the process that will be faced by real users while installing it,
- Or you can run it via OTA (Over the Air), which will try to show you all the steps that will faced by users while installing your application in their devices.
- Third one (Running in Debug Mode) helps us in finding out bugs and errors (if any).
Below is the snapshot showing "how to run project" via right clicking on it.
Running your first application in real device (Mobile/Cellphone)
To run your first application on your phone, then, you can do so by following steps shown below.
Steps need to be followed if you build application via Java ME SDK 3.0
- Go to: "C:\Users\seven\Documents\JavaMESDKProjects\your~project~name\dist\",
- Then, you'll see two files with your project name but with twoo different file extension i.e. with ".jad" and ".jar",
- Send that jar file to your phone and install it.
- after that you can go to applications folder in your cellphone and try running it.
Steps need to be followed if you build application via Netbeans IDE and Java ME SDK 3.0.5
- In this case, you will find applications here "C:\Users\seven\Documents\NetBeansProjects" and all other steps are same.
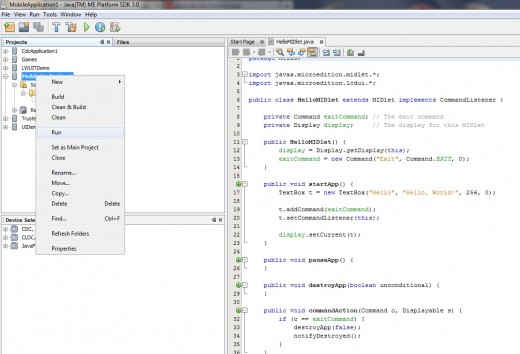
"Source Code" of this program is explained in next chapter (Article), Where you will learn about "How it is easy to code applications in java and j2me" (If you never programmed and tried your hands with this language).